Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) revolution has accelerated the demand for wireless technologies that can offer long-range connectivity with low power consumption and minimal infrastructure. Among the emerging communication protocols, LoRa (Long Range) has gained substantial traction for enabling cost-effective, wide-area networks. Developed by Semtech, LoRa is a physical layer protocol that utilizes chirp spread spectrum modulation to achieve communication ranges of several kilometers while maintaining ultra-low power usage.
For developers, LoRa opens up opportunities to build connected systems where traditional short-range wireless protocols like Wi-Fi or Bluetooth fall short, particularly in rural or infrastructurally sparse environments. From agriculture to smart cities, and industrial automation to asset tracking, LoRa-based solutions are proving to be both scalable and sustainable. In today’s blog we will cover details related to design, development, and testing LoRa-based solutions, and evaluates the trade-offs and domain-specific use cases developers should consider.
What Is LoRa and LoRaWAN?
At a fundamental level, LoRa (Long Range) is a modulation technique based on Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS), designed to transmit small packets of data across long distances with very low power consumption. It's ideal for battery-operated devices that send data infrequently, such as sensors measuring temperature, humidity, soil moisture, or location.
LoRaWAN (LoRa Wide Area Network) is the communication protocol and system architecture built on top of LoRa. It governs how devices connect to the network, how they communicate, and how data is authenticated, routed, and secured across the ecosystem. It operates on unlicensed ISM bands (such as 868 MHz in Europe, 915 MHz in the US and 433Mhz in Asia), and supports a star-of-stars topology via LoRaWAN, the MAC layer protocol that governs communication between end nodes and gateways.
LoRa Technologies
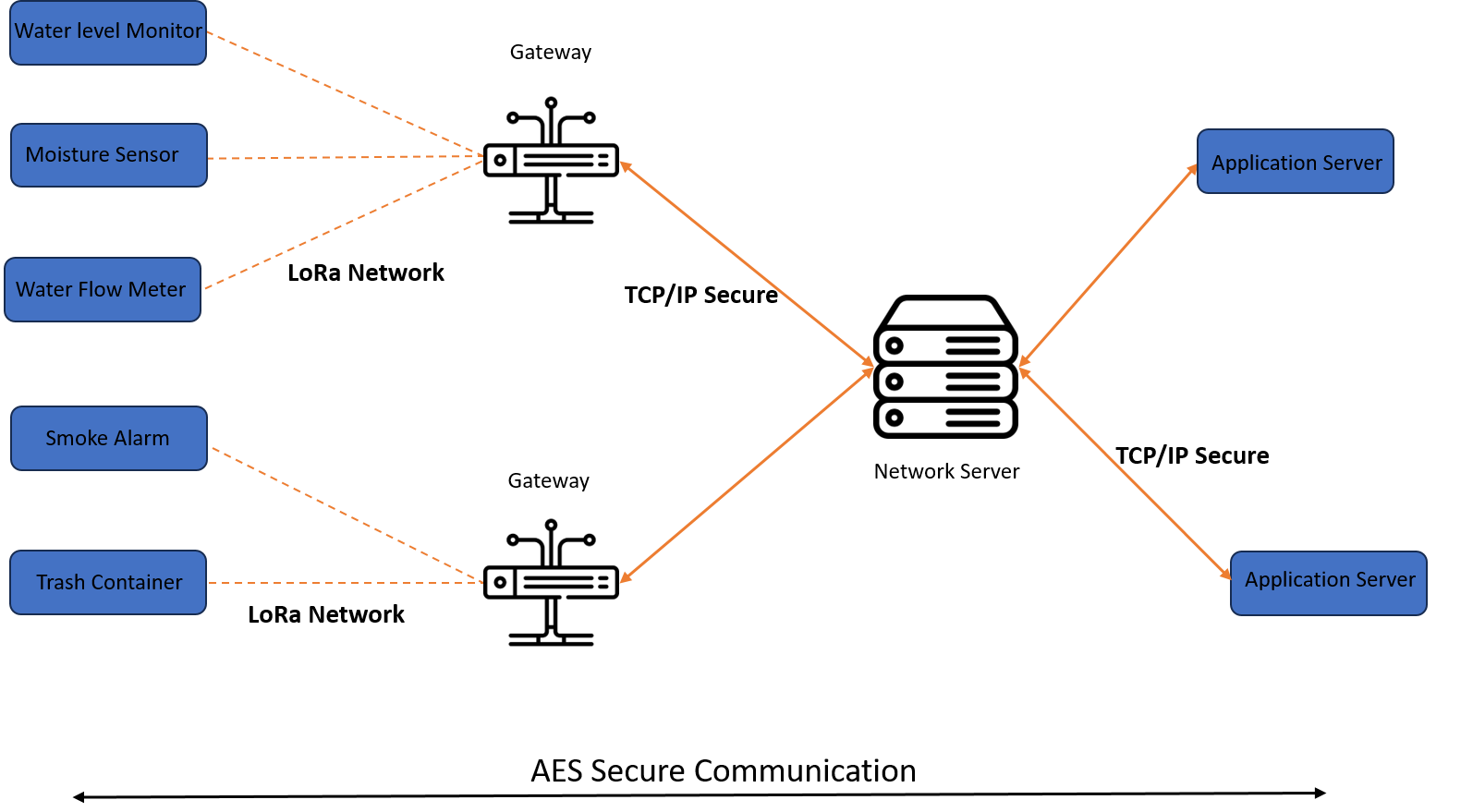
Core Components of a LoRaWAN System
A typical LoRaWAN network comprises:
- End Devices: These are the sensors or actuators deployed in the field. They communicate wirelessly via LoRa to nearby gateways.
- Gateways: These act as relay stations, receiving radio signals from end devices and forwarding them to a central network server over IP (Wi-Fi, Ethernet, 4G).
- Network Server:This is the brain of the system. It handles packet de-duplication (from multiple gateways), device authentication, session management, and Adaptive Data Rate (ADR) control.
- Application Server: This server processes decrypted data, applies business logic, and often sends it to cloud platforms or databases.
How LoRaWAN Works: The Communication Flow
- Uplink Communication: An end device wakes up, senses data (e.g., temperature), and transmits it using LoRa modulation. The message is picked up by one or more gateways and forwarded to the network server. For example, temperature sensor, wakes up from sleep, collects data, and transmits it using LoRa modulation.
- Downlink Communication: The network server may respond (e.g., to control a valve or LED) via the same gateway. This is less frequent to save energy. For example, triggering a relay or adjusting settings.
- Classes of Devices:
- Class A: It is most energy-efficient and are mandatory for all LoRaWAN-compliant devices. They only open receive windows for a short duration after each uplink transmission, making downlink possible only immediately following an uplink. This class is ideal for battery-powered sensors that don’t require frequent commands from the network.
- Class B: This type build on Class A by introducing additional, scheduled receive windows. These are synchronized using periodic beacons sent by the network, allowing for more predictable downlink timing. As a result, Class B supports use cases that require periodic control or updates, such as smart lighting or environmental monitoring systems.
- Class C: This type keep their receive windows open nearly all the time, enabling instant response to network commands. While this ensures minimal latency and high responsiveness, it significantly increases power consumption. Therefore, Class C is best suited for devices with a constant power supply, such as industrial actuators, alarms, or gateways.
Pros and Cons of LoRa Technology
Pros:
- Long Range: LoRa devices can communicate over distances of 2–15 km in rural areas and up to 5 km in urban settings.
- Low Power Consumption: Ideal for battery-powered devices with operational life spanning several years.
- License-Free Spectrum: No recurring spectrum fees make it economically viable for large-scale deployments.
- Good Penetration: LoRa's sub-GHz operation allows signals to penetrate buildings and underground locations.
- Strong Ecosystem: Supported by the LoRa Alliance, with wide availability of open-source stacks and cloud integrations.
Cons:
- Low Data Rate: Not suitable for high-bandwidth applications like video streaming or real-time audio.
- Latency::Unsuitable for time-critical applications due to duty cycle restrictions and ALOHA-based MAC.
- Network Collisions:As device density increases, packet collisions become more likely, especially on shared channels.
- Regional Variation:Different frequency bands across regions (EU vs. US) complicate global deployments.
Adoption of LoRa in Key Domains
- Agriculture:LoRa is widely used in precision agriculture for soil moisture monitoring, irrigation control, weather tracking, and livestock management. Nodes can be deployed across vast fields and transmit periodic updates to a centralized dashboard. The ability to operate on battery for years makes it perfect for remote installations where frequent maintenance is impractical.
- Smart Cities: LoRa’s long-range coverage and low cost make it suitable for urban infrastructure such as smart lighting, parking meters, garbage bin level sensing, and utility metering. Municipalities can deploy gateways on buildings or towers to cover large urban areas with minimal infrastructure.
- Industrial Automation:In factories and industrial plants, LoRa can be used for condition monitoring, safety compliance (like gas leak detection), and predictive maintenance. The ability to coexist with existing industrial networks (such as Modbus or CAN) makes LoRa a non-intrusive addition to legacy setups.
- Asset Tracking and Logistics:LoRa-based asset trackers offer a low-cost alternative to GPS/GSM trackers, especially for indoor or campus-level tracking. LoRa’s long range and ability to triangulate location using multiple gateways enable businesses to track containers, vehicles, or machinery across a facility or supply chain.
- Healthcare:Though not mainstream yet, LoRa is finding its place in remote patient monitoring and elderly care systems. Battery-powered wearables or home-monitoring units can transmit vital signs at regular intervals, especially in areas with poor cellular coverage.
- Environmental Monitoring:LoRa is heavily used in air quality monitoring, water level sensing, and disaster early warning systems. Devices can be deployed in forests, rivers, and remote areas to transmit data back to central dashboards for real-time analytics.
Conclusion
LoRa technology is a good option for building smart and power-efficient IoT systems that need to work over long distances and keep the cost low. It allows developers to create solutions that run for a long time, consume less power, and perform well even in challenging conditions. To get the best out of LoRa, it's important to understand both hardware and software aspects, and to properly test the system – not just for basic functions, but also for range, power usage, and how well it works with other devices.
Though LoRa is not suitable for high-speed or real-time data, it's ideal for use cases where only small amounts of data need to be sent over long distances. That's why it's widely used in smart city projects, agriculture, and remote monitoring. As more industries adopt smart systems, LoRa’s usage is expected to grow.
At Embien, we support our customers in building LoRa-based products by taking care of everything from hardware design and firmware development to testing and integration, ensuring reliable and scalable IoT solutions.

